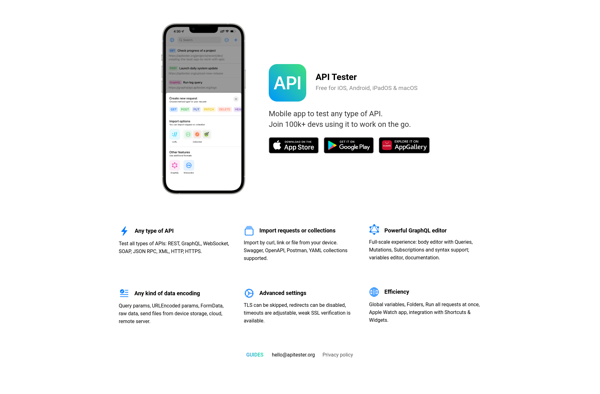
Description: API Tester is a software tool used by developers to test and debug APIs. It allows sending requests to API endpoints and inspecting the responses to validate functionality, performance, and integration.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
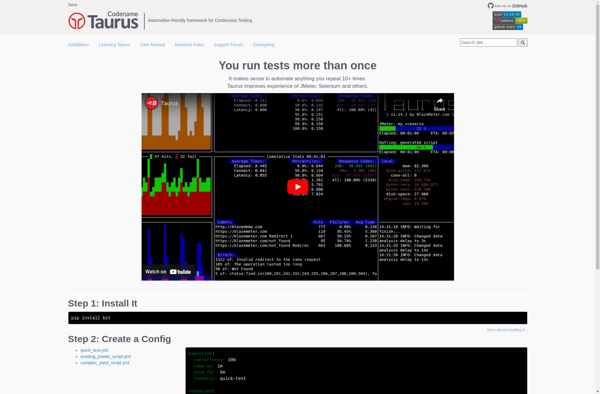
Description: Taurus is an open-source performance testing framework for automated tests and load testing of web applications. It is designed to take the pain out of load testing by making it easy to create, manage, and monitor performance tests.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API