Description: Barrier is an open source software KVM solution that allows users to control multiple computers from a single keyboard, mouse, and monitor. It enables seamless control of computers as if using one machine.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
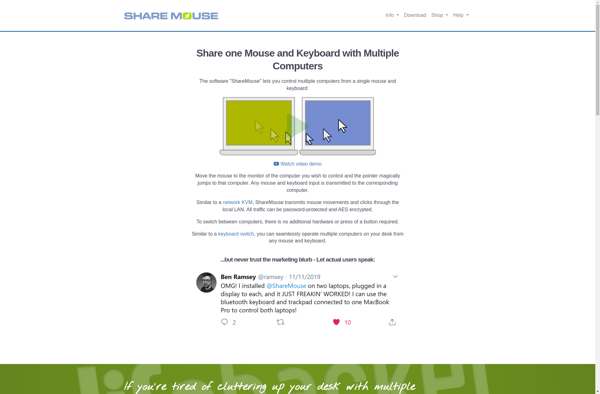
Description: ShareMouse is a lightweight software that allows you to share your mouse and keyboard between multiple computers. It works by synchronizing mouse movements and keystrokes across different devices connected on a local network.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API