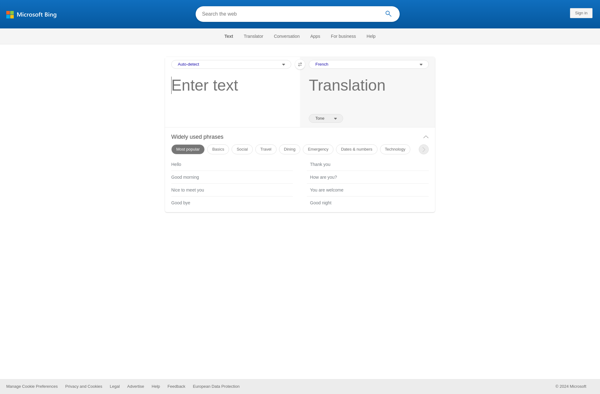
Description: Bing Translator is a free translation service by Microsoft that allows users to translate text, documents, and web pages between over 100 languages. It offers multiple ways to translate such as through its website and mobile apps, browser extensions and plugins, and a REST API.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Dilmanc is an open-source automatic differentiation software library for C and C++ programs. It allows users to numerically evaluate derivatives of C/C++ functions for applications such as gradient-based optimization and sensitivity analysis, without needing to derive and implement analytical derivatives.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API