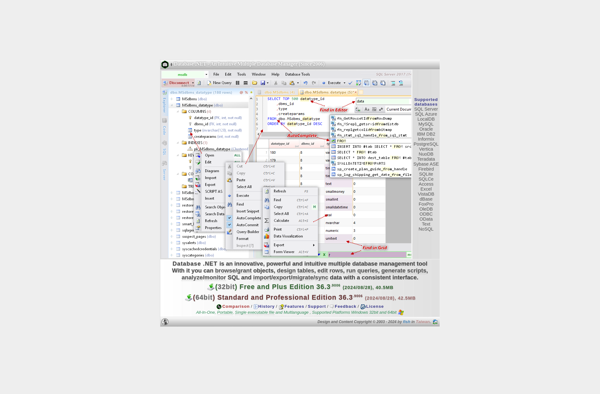
Description: Database .NET is an open source ORM framework for .NET that provides an abstraction layer over databases like SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL, etc. It simplifies data access in .NET applications.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
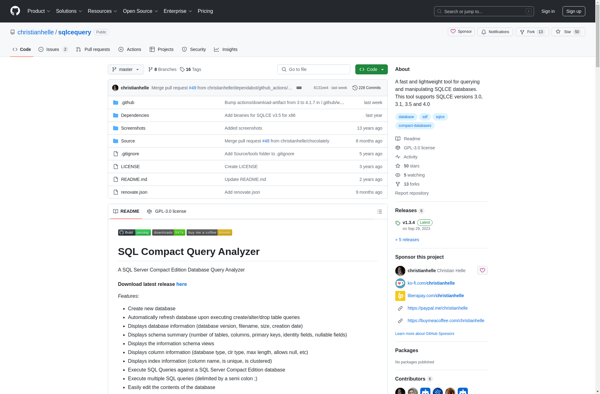
Description: SQL Compact Query Analyzer is a free lightweight tool that allows users to write, edit, and execute SQL queries against SQL Compact databases. It has syntax highlighting and auto-completion to help with writing queries.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API