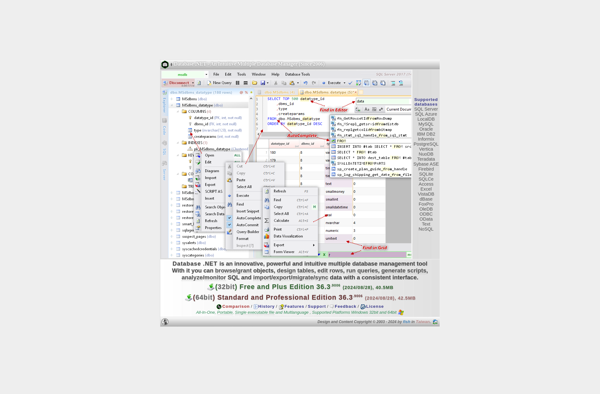
Description: Database .NET is an open source ORM framework for .NET that provides an abstraction layer over databases like SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL, etc. It simplifies data access in .NET applications.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Toad for SQL Server is a database management and administration tool that provides SQL scripting, object browsing, SQL tuning and performance optimization, and other features to help you manage SQL Server databases.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API