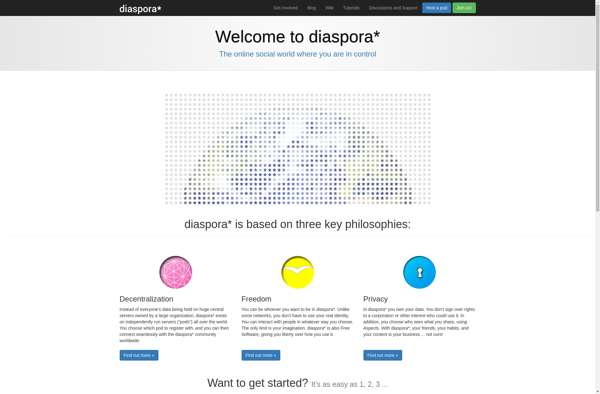
Description: Diaspora is a decentralized, open source social network that emphasizes privacy and user control. It allows users to host their data and share information without relying on large corporate platforms.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Libertree is a free, open source social networking platform focused on privacy and decentralization. It aims to give users control over their data by hosting content on independent user-controlled servers rather than centralized services.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API