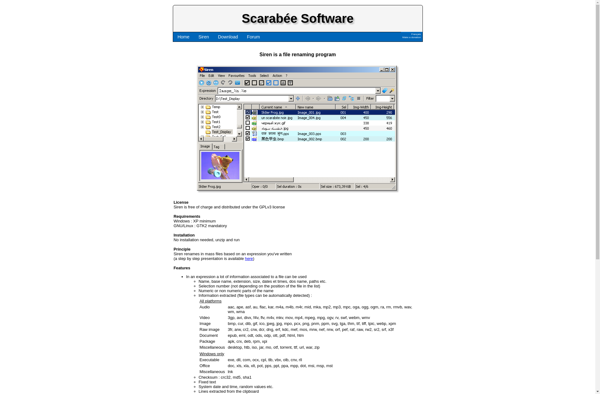
Description: Fast File Renamer is a free software program for Windows that allows users to easily rename multiple files and folders at once. It has an intuitive interface with support for wildcards, regular expressions, EXIF data, ID3 tags and more for advanced find and replace batch renaming.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Siren is an investigative link analysis software used by law enforcement and intelligence agencies to visualize connections between people, places and events. It helps analysts uncover hidden relationships and patterns within large, disparate datasets.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API