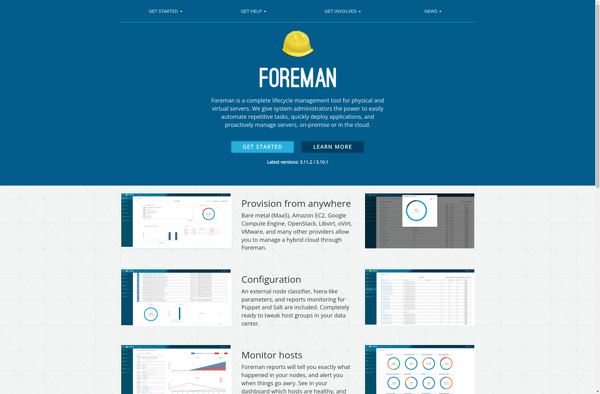
Description: Foreman is an open source systems management tool that helps administrators automate repetitive tasks, deploy applications, and manage servers throughout their lifecycle. It provides comprehensive visibility into IT assets through monitoring and reporting.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: mgmt is an open-source configuration management and orchestration tool. It allows you to easily manage your infrastructure and apps across hybrid environments.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API