Description: iData Mac Data Recovery is a data recovery software designed specifically for Mac operating systems. It can recover lost or deleted files from hard drives, SSDs, USB drives, SD cards, and other storage devices connected to a Mac computer.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
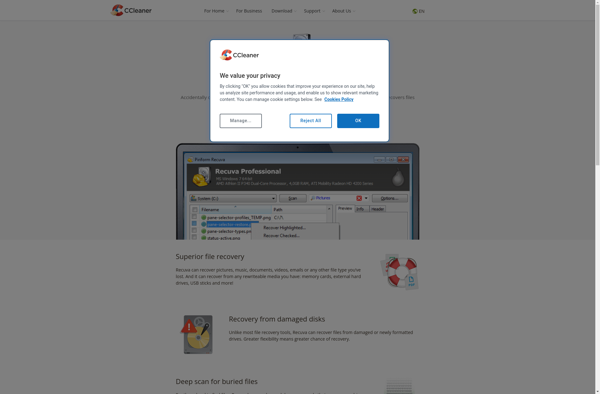
Description: Recuva is a free data recovery software developed by Piriform. It can recover deleted files from your Windows computer, external drives, USB flash drives and memory cards. Recuva works to undelete files that have been deleted from the Recycle Bin, via a software crash, virus infection or disk formatting.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API