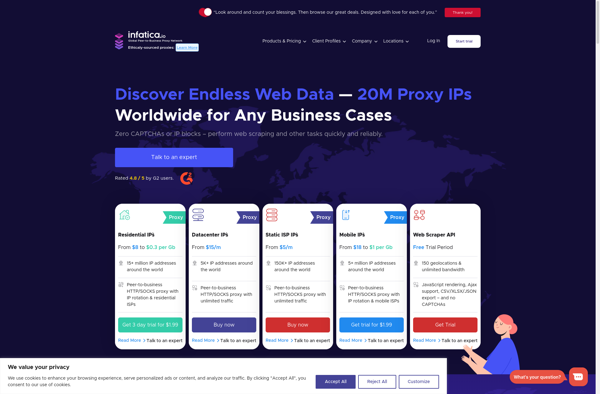
Description: Infatica is an open-source business intelligence and data analytics platform. It provides tools for reporting, visualizations, dashboards, and ad-hoc data exploration. Infatica is known for its flexibility, scalability, and ease of use.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
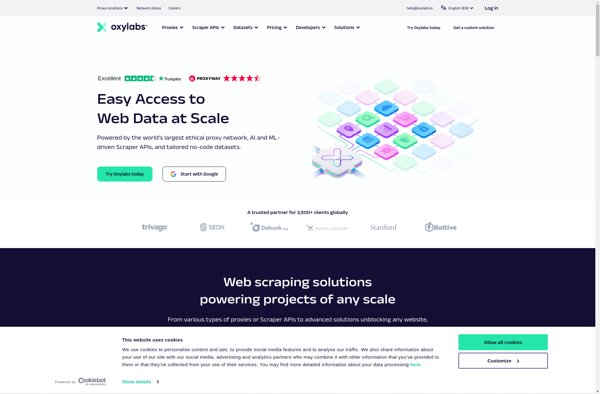
Description: Oxylabs is a proxy and data extraction API service that allows users to access otherwise restricted web data. Its API allows fetching web data at scale while managing IPs and proxies.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API