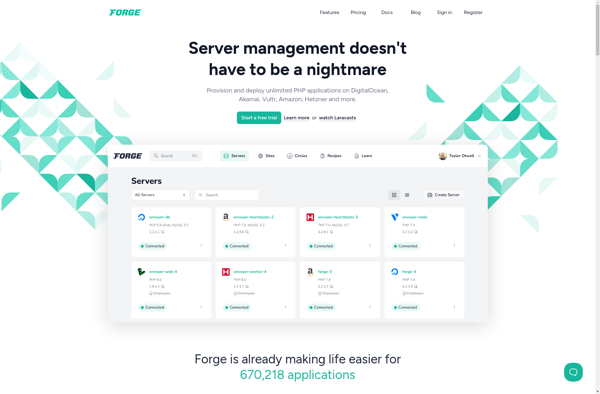
Description: Laravel Forge is a web UI and API for managing Laravel infrastructure and deployment. It allows easy provisioning and management of servers, sites, databases, and other infrastructure needed to deploy Laravel applications. Key features include one-click app deployment, SSH access to servers, and automation for tasks like provisioning, deploying, and scaling.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: ClusterCS is an open-source platform for deploying and managing containerized applications across clusters of hosts. It provides a simple way to orchestrate containers, services, and batch jobs using Kubernetes.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API