Description: Mailinator is a free, disposable email service that allows users to create email aliases on the fly without registration. It can be useful for testing or other purposes where you don't want to provide your real email.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
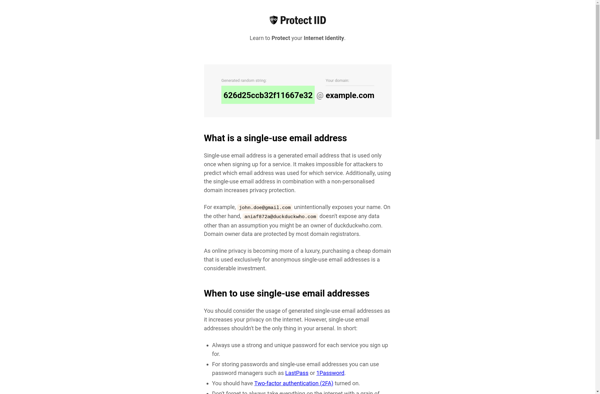
Description: Protect IID is a privacy software that helps prevent the leakage of personally identifiable information (PII) by masking or replacing sensitive data fields. It works by scanning databases, files, and applications to discover PII and then applying transforms to encrypt, tokenize, or redact that data.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API