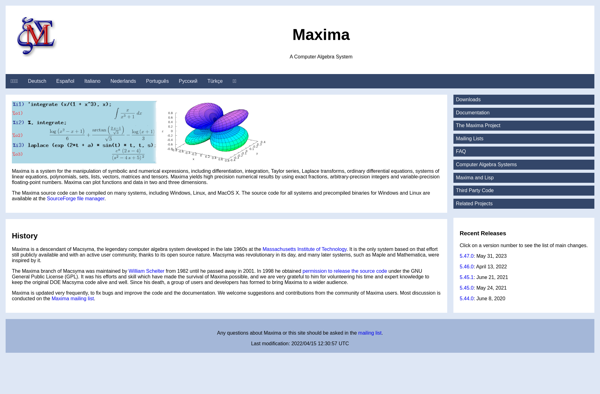
Description: Maxima is an open-source computer algebra system that provides symbolic computation capabilities. It can manipulate mathematical expressions, differentiate and integrate functions, solve equations, work with matrices, graphs, and more. Useful for STEM fields like math, engineering, physics.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: GiNaC is an open-source computer algebra system for symbolic mathematical computations. It has a C++ interface and supports arbitrary precision integer, rational, complex number, symbolic computation, and matrix operations.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API