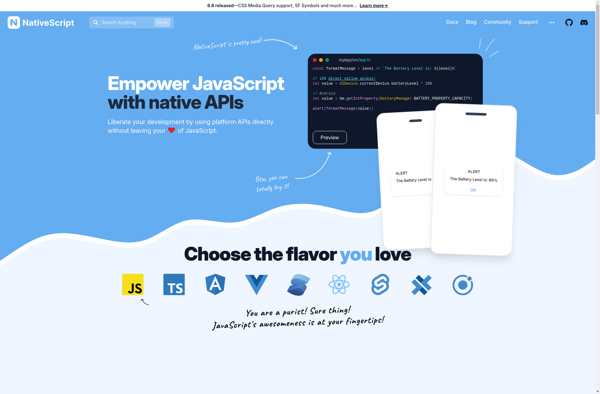
Description: NativeScript is an open source framework for building native iOS and Android apps using JavaScript or TypeScript. It allows developers to reuse skills and code from web development and build truly native mobile applications with access to native APIs.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: The Ionic Framework is an open source mobile app development framework that enables developers to build high-quality native and progressive web apps with web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It offers tools and services for developing mobile apps that look great on any device.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API