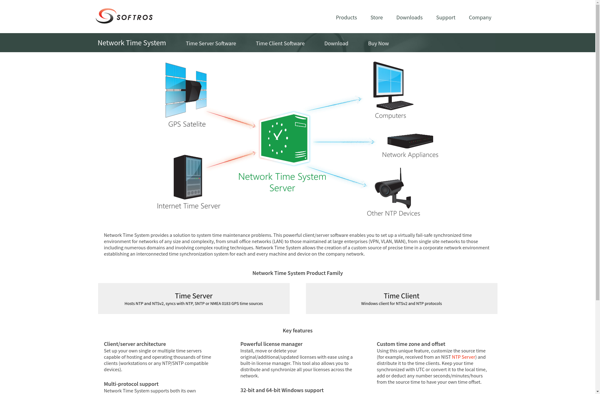
Description: The Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a networking protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems over packet-switched, variable-latency data networks. NTP is intended to synchronize all participating computers to within a few milliseconds of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: The Network Time Protocol daemon (ntpd) is a program that synchronizes computer clocks over a network. It works by coordinating clocks across a variety of servers and clients using the Network Time Protocol to ensure accurate timekeeping.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API