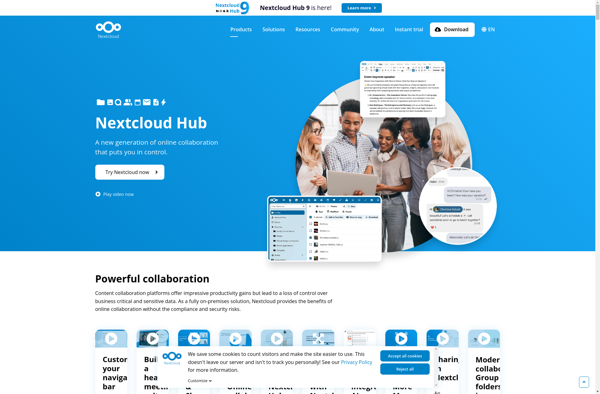
Description: Nextcloud Hub is an open source, self-hosted file sharing and communication platform. It provides file storage, sync, and share capabilities, as well as messaging, online document editing, calendar/contacts, and more. Useful for organizations looking for on-premises alternatives to things like Dropbox, Office 365, or G Suite.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Linchpin is an open source infrastructure as code framework that enables developers and operations teams to easily provision cloud infrastructure. It has declarative infrastructure configuration and can integrate with various cloud providers like AWS, Azure, GCP, and OpenStack.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API