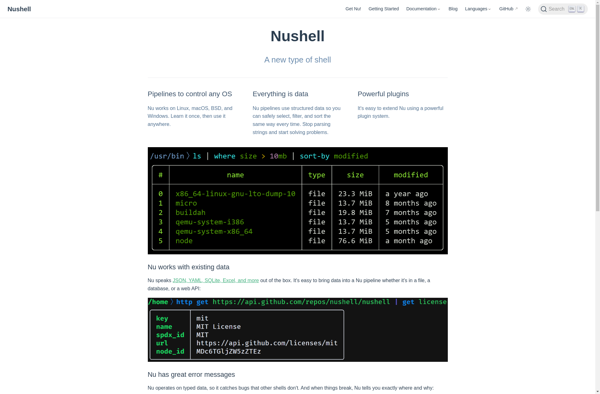
Description: Nu Shell is a new, open source shell focused on improving the command line experience and development workflow. It features structured data, a modular design, powerful automation and scripting capabilities.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Xiki is a command line interface and shell alternative that allows you to navigate and operate on structured data. It aims to provide a simple yet powerful way to access various types of data and systems.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API