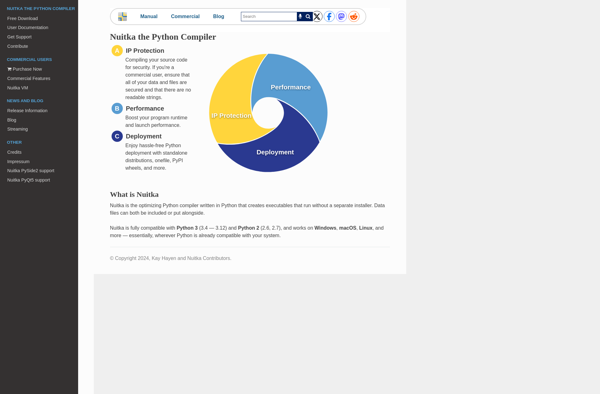
Description: Nuitka is an open source Python compiler that translates Python code into C or C++ code. It allows developers to create standalone Python executables that can be run without requiring the Python interpreter. Key benefits are improved performance, obfuscation, and easy distribution of Python programs.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: bbfreeze is a converter for Python programs into stand-alone executables, under Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, FreeBSD, Solaris and AIX. The goal is to make Python programs independently distributable so that they can be run without requiring the Python interpreter.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API