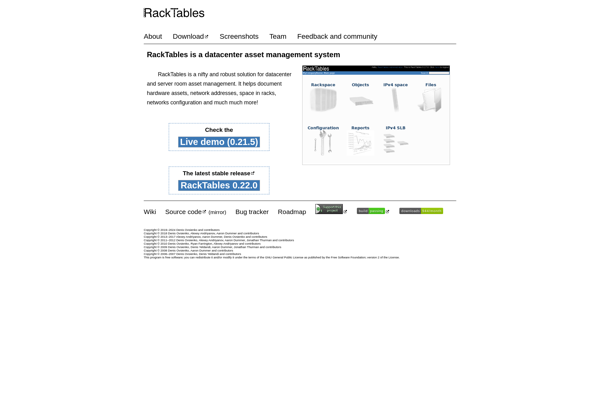
Description: RackTables is an open-source infrastructure asset management solution for data centers and server rooms. It helps organize and track hardware assets and visualize resource usage to plan for capacity and growth. It offers a web-based interface, monitoring and auditing tools, network map generation, and CSV import/export.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Nlyte Asset Optimizer is a data center infrastructure management (DCIM) software that provides capabilities for modeling, visualizing, analyzing, and optimizing data center assets and resources. It aims to improve data center efficiency, capacity planning, and asset utilization.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API