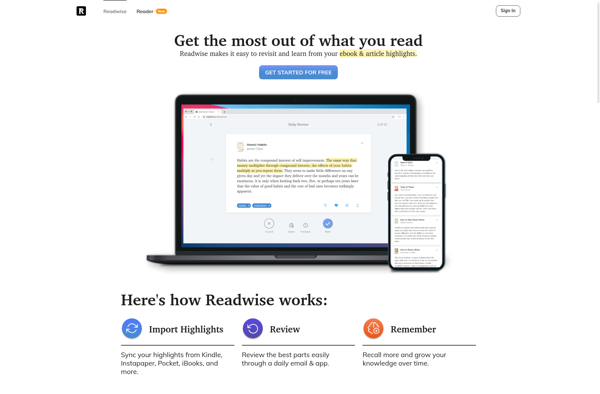
Description: Readwise is a read-later app that helps you track, organize and review highlights from articles, books and websites. It syncs highlights from Kindle and Pocket automatically, allowing you to easily revisit your highlights later.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
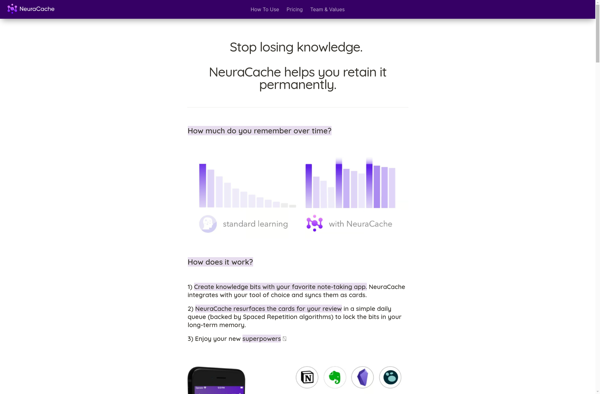
Description: NeuraCache is an open-source caching system designed to accelerate access to data from databases or other data sources. It uses advanced algorithms to predict what data will be needed and caches it in memory, significantly speeding up response times.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API