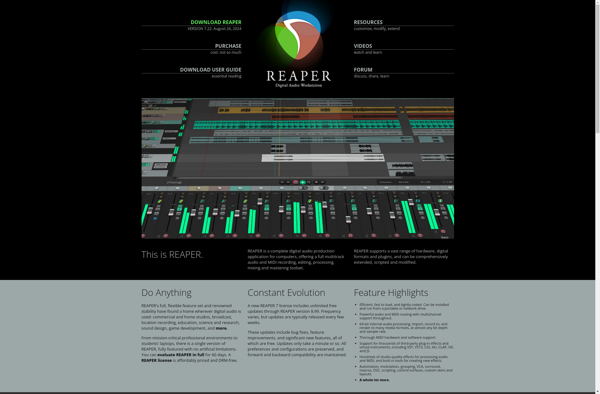
Description: Reaper is a digital audio workstation and MIDI sequencer software for Windows, Mac and Linux. It has a fully featured interface for multi-track audio and MIDI recording, editing and mixing. Reaper is known for its flexibility, customization and value.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Open Octave is a free open-source software alternative to MATLAB. It provides a high-level programming language and advanced mathematical computing environment for numerical computations, data analysis, machine learning, and image processing.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API