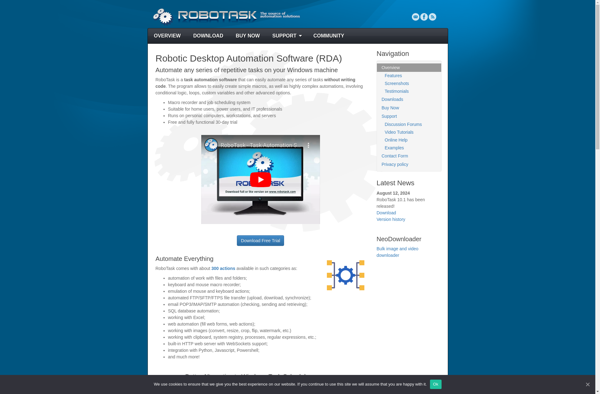
Description: RoboTask is an automation tool that allows you to create workflows and macros to automate repetitive tasks on your computer. It features a drag and drop interface to easily connect triggers, actions, and flow control without coding.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: AutoHotkey is a free, open-source custom scripting language for Windows, initially aimed at providing easy keyboard shortcuts and hotkeys. It simplifies automation tasks such as macros, remapping keys, and application-specific scripts.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API