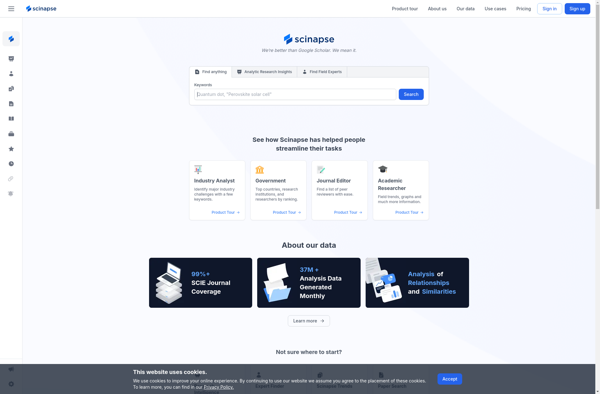
Description: Scinapse is an academic search engine and paper repository that helps researchers quickly access scholarly articles and preprints. It aggregates millions of open access papers and uses AI to provide personalized recommendations.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Google Scholar is a free online academic database that indexes scholarly literature across disciplines and sources. It allows users to search for peer-reviewed papers, theses, books, abstracts, and court opinions.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API