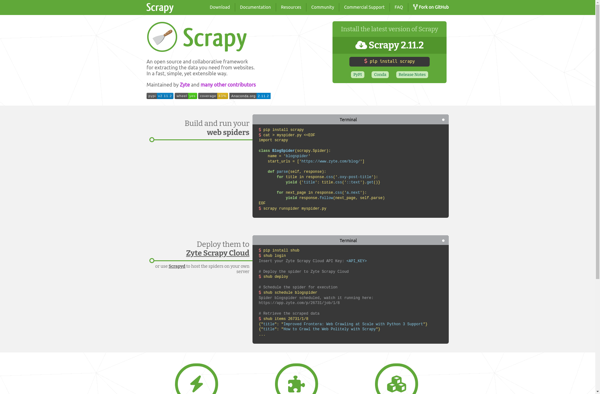
Description: Scrapy is an open-source web crawling framework used for scraping, parsing, and storing data from websites. It is written in Python and allows users to extract data quickly and efficiently, handling tasks like crawling, data extraction, and more automatically.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
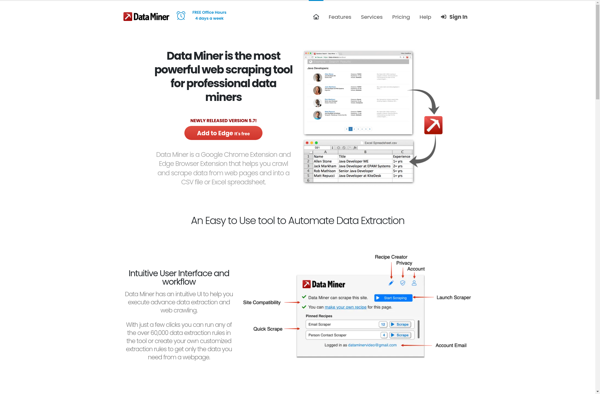
Description: Data Miner is a software tool for monitoring, analyzing, and visualizing networks, services, and IoT devices in real-time. It provides automated fault, performance, and root cause analysis along with customizable dashboards and reports.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API