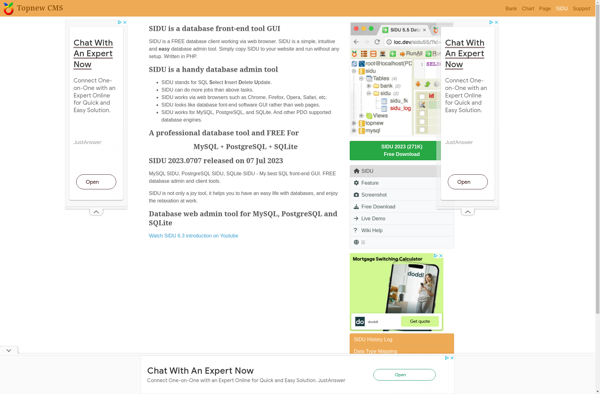
Description: SIDU is an open-source, self-hosted knowledge base and documentation software. It allows teams to collaboratively create, organize, and share knowledge across the organization. Key features include powerful search, customizable templates, role-based permissions, and integration with popular tools.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
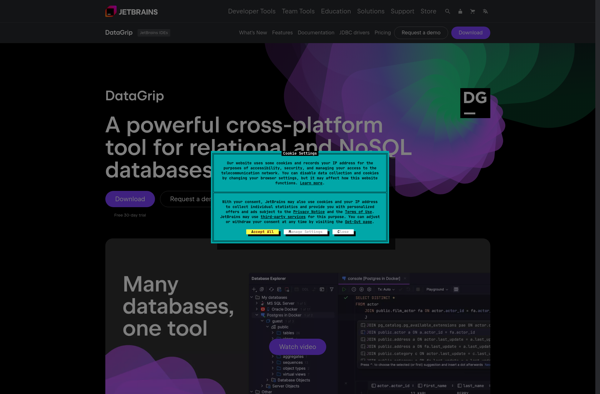
Description: DataGrip is a cross-platform IDE by JetBrains aimed at SQL and database developers. It provides an ergonomic interface for accessing databases, writing queries, inspecting schemas, and managing database connections.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API