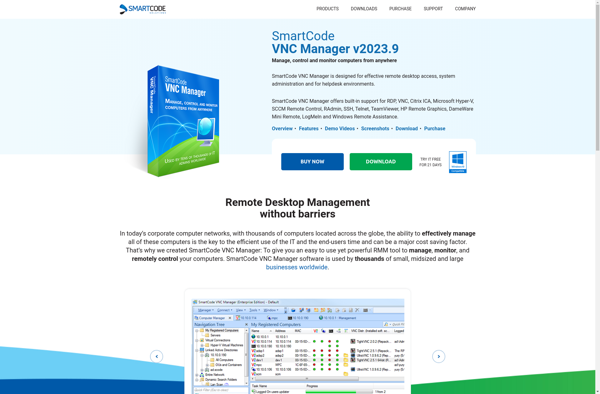
Description: SmartCode VNC Manager is a VNC client for Windows that allows you to easily connect to and manage multiple remote desktops. It includes features like a unified bookmarks toolbar, support for multiple protocols, Wake-on-LAN, and more.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: mRemoteNG is an open-source, tabbed, multi-protocol, remote connections manager. It allows you to view all your remote connections in a simple yet powerful interface. mRemoteNG supports the Remote Desktop Protocol, VNC, SSH, Telnet, rlogin, and RAW Socket connections.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API