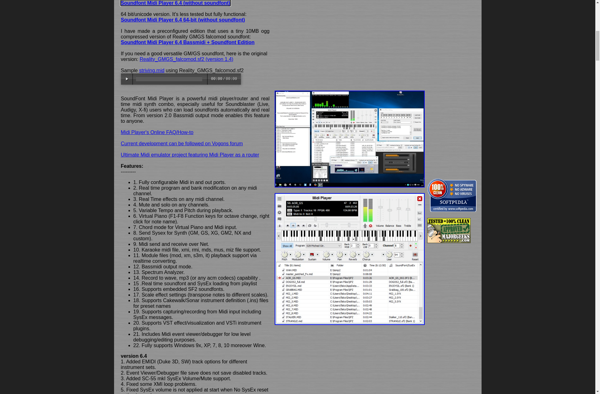
Description: Soundfont Midi Player is a lightweight program for Windows that allows you to play MIDI files using downloaded soundfonts. It supports effects like reverb and has a simple interface for loading MIDI files and selecting soundfonts.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Singa is an open-source distributed deep learning platform that can train large machine learning models over CPUs, GPUs, or clusters. It provides a flexible programming model that supports a wide range of deep learning frameworks and algorithms.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API