Description: TLP is an open-source power management tool for Linux that aims to improve battery life. It comes with a set of predefined rules and scripts that automate tuning of kernel parameters regarding CPU, disk, and other power-related settings.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
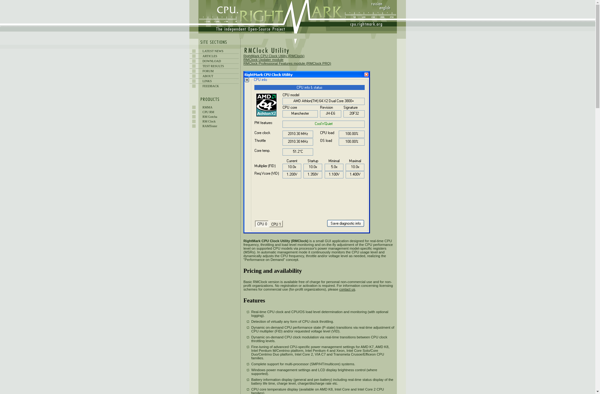
Description: RMClock is an open-source, customizable clock widget for Windows that displays the time, date, and system metrics on your desktop. It has skins and plugins to customize the look and information displayed.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API