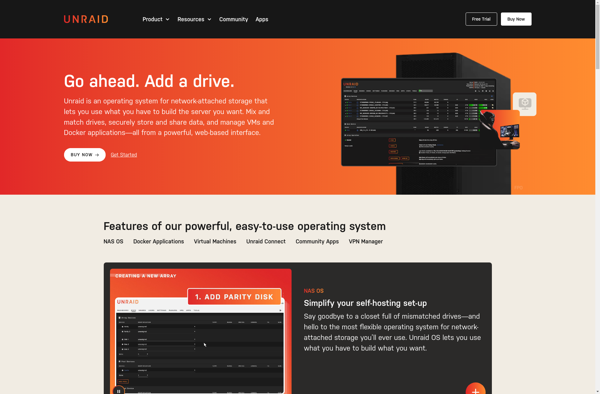
Description: Unraid is an operating system optimized for media storage and servers. It supports combining hard drives of different sizes into a single storage pool, parity-based data protection, on-the-fly disk encryption, and Docker containers.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Windows Storage Spaces is a storage virtualization technology in Windows that allows combining multiple disks into storage pools. It provides fault tolerance using mirroring or parity and allows spanning pools across disks of different sizes.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API