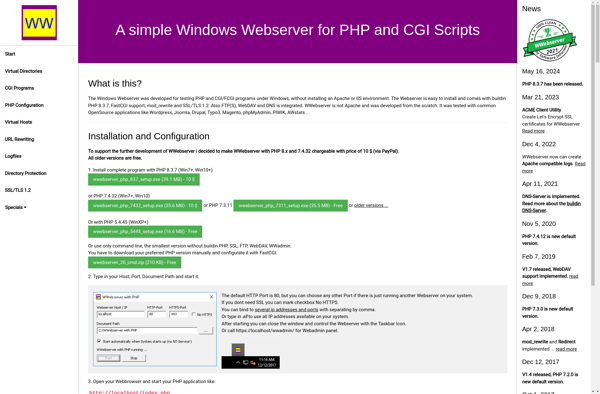
Description: Windows Webserver is a web hosting platform developed by Microsoft that runs on Windows Server operating systems. It supports various web technologies like ASP.NET, PHP, Node.js and can be used to host websites and web applications.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Lighttpd, often referred to as Lighty, is an open-source and lightweight web server known for its speed, efficiency, and low resource consumption. Designed with a focus on performance and flexibility, lighttpd is suitable for serving static and dynamic content, acting as a reverse proxy, and handling high-traffic websites.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API