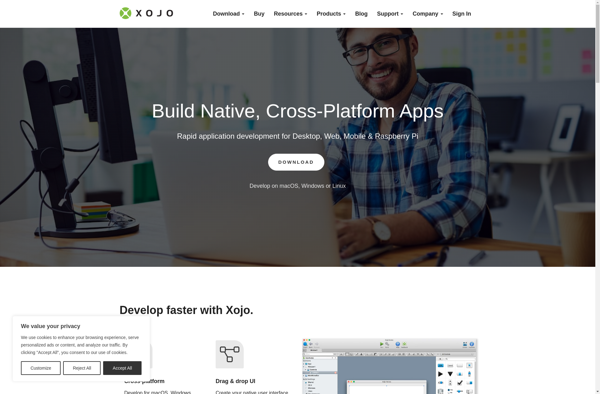
Description: Xojo is a cross-platform integrated development environment (IDE) and programming language used to build native apps for desktop, web, iOS and Raspberry Pi. It uses a Basic-like programming language and allows developers to quickly build apps with a drag-and-drop interface, making it easy for beginners.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: VisualNEO Win is a Windows-based neural network software that allows users to design, train, and simulate neural networks. It features a graphical user interface for building networks and includes algorithms like backpropagation for network training.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API