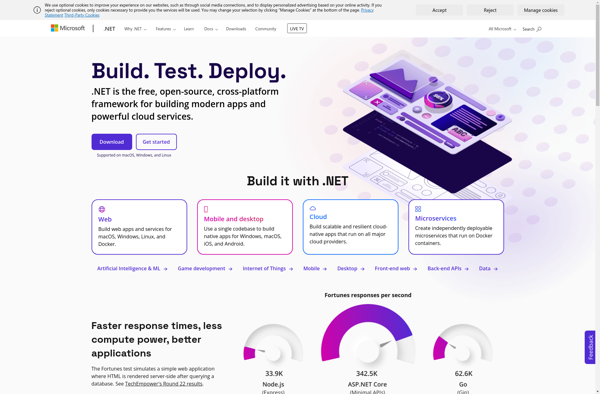
Description: The .NET Framework is a software framework developed by Microsoft that runs primarily on Microsoft Windows. It includes a large class library called Framework Class Library and provides language interoperability across several programming languages.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Ceylon is an open source programming language that runs on the Java Virtual Machine or JavaScript runtimes. It features a strong and static type system, immutability by default, higher-order functions, metaprogramming, and modular and hierarchical visibility control.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API