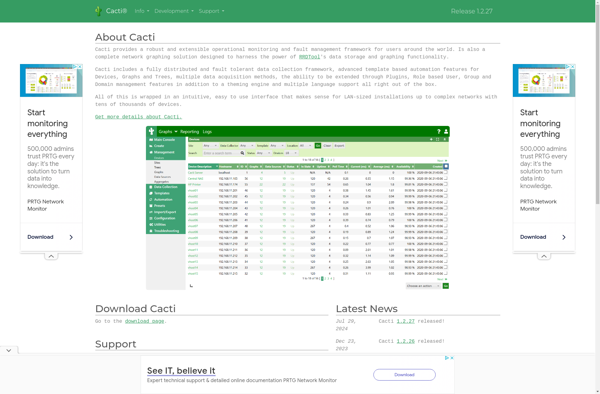
Description: Cacti is an open-source network monitoring and graphing tool that provides easy monitoring of network devices and servers. It polls devices for utilization data, stores the data, and generates graphs and statistics to help analyze network traffic and utilization.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: vnStat is an open-source network traffic monitor for Linux that keeps a log of network traffic for the selected interface(s). It uses the network interface statistics provided by the kernel to keep track of the monthly, daily and hourly bandwidth usage.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API