Description: CloudShark is a cloud-based network packet analyzer that allows users to upload packet capture files and analyze them using a web browser. It provides features like filtering, extraction, statistics, search, and sharing of PCAPs.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
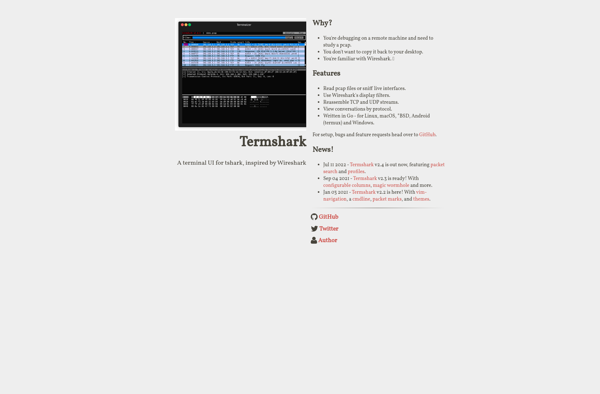
Description: Termshark is a terminal based network protocol analyzer. It allows you to inspect network traffic and analyze packets, similar to Wireshark, but runs in a terminal instead of a graphical interface.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API