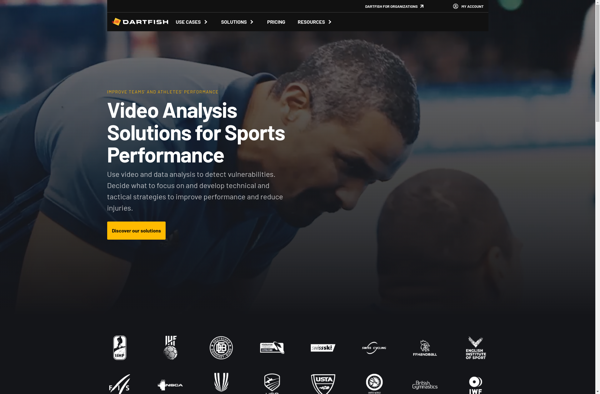
Description: Dartfish is video analysis software used by athletes, coaches, and sport scientists to study technique and improve performance. It allows users to compare videos side-by-side, overlay them, annotate key frames, measure angles and distances, and track motion.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
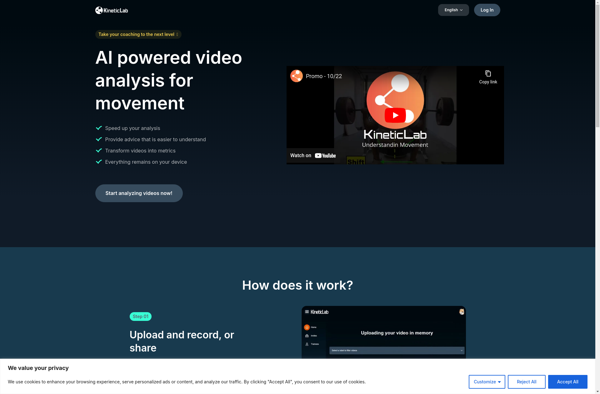
Description: KineticLab is a free, open-source physics simulation software for creating interactive physics demonstrations and models. It allows users to visually build simulations by placing objects, attaching springs/motors/fields, and defining interactions.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API