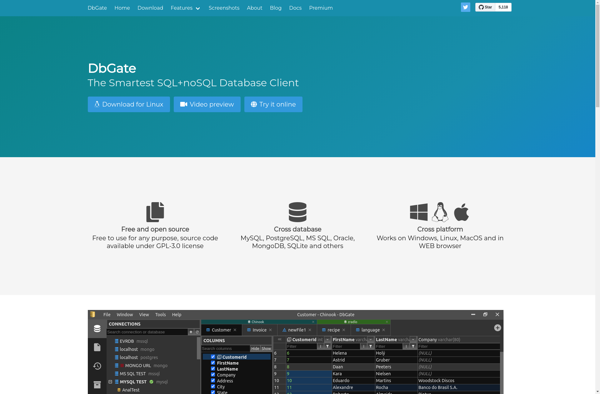
Description: DbGate is a database client tool that allows you to easily manage multiple databases from one interface. It supports connecting to popular databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and more.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: DataGrip is a cross-platform IDE by JetBrains aimed at SQL and database developers. It provides an ergonomic interface for accessing databases, writing queries, inspecting schemas, and managing database connections.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API