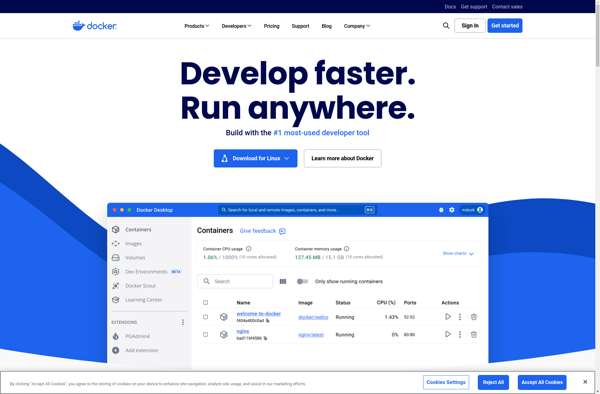
Description: Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. It allows developers to package applications into containers—standardized executable components combining application source code with the operating system (OS) libraries and dependencies required to run that code in any environment.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Otto is an open source tool created by HashiCorp for deploying and managing applications across multiple cloud environments. It allows developers to define infrastructure as code and automate provisioning, deployment, and orchestration.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API