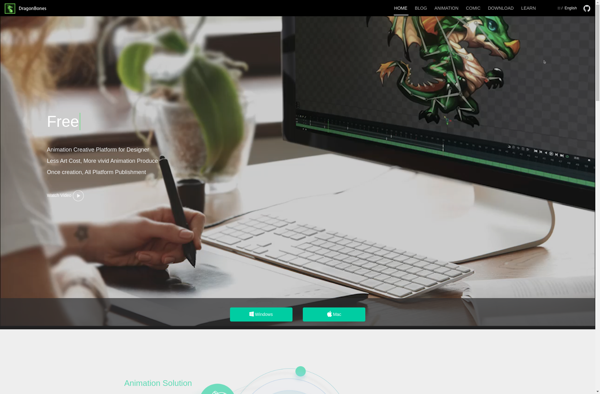
Description: DragonBones is an open-source 2D skeleton animation system and game engine plugin created by the Chinese company Egret Technology. It allows developers to create and animate 2D sprites using skeletal animation techniques commonly seen in 3D games and animation.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Marionette Studio is a user interface (UI) automation testing tool for web and mobile apps. It provides a codeless way to create automated UI tests with built-in object recognition, cross-browser testing, image-based testing, and AI-powered self-healing tests.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API