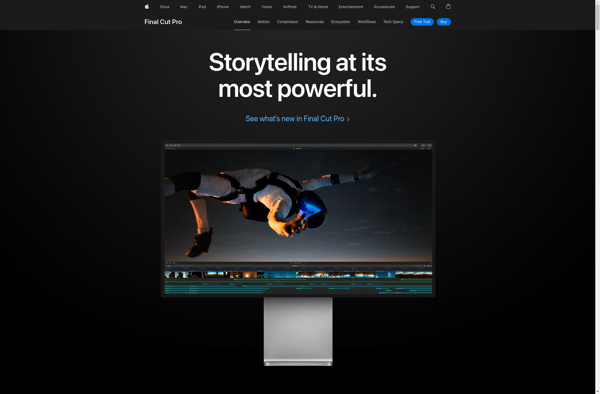
Description: Final Cut Pro is professional video editing software developed by Apple. It allows users to import, edit, and export video in a wide variety of formats. Final Cut Pro provides advanced tools for editing, color correction, audio work, effects, and more.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: HyperEngine-AV is an antivirus engine designed for detecting and blocking viruses, malware, spyware, ransomware, and other cyber threats. It uses signature-based detection, heuristics, machine learning models, and cloud querying to monitor system files, memory, boot records, and network traffic.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API