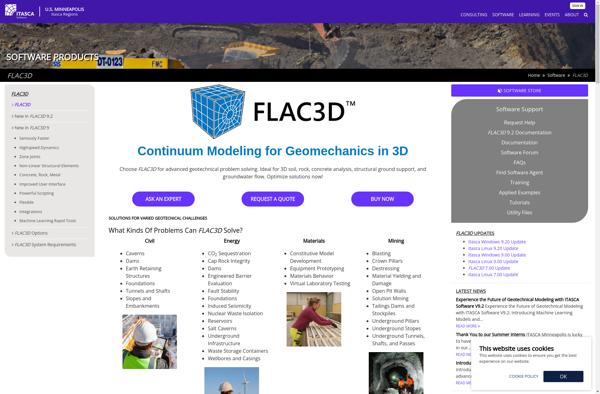
Description: Flac3D is an open-source finite element analysis software for numerical modeling of geotechnical applications such as underground excavations, slope stability, and foundation settlement. It allows 3D analyses of soil and rock masses using continuum or discontinuum material models.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: PLAXIS 3D is a finite element software used for geotechnical analysis and design in 3D. It can model complex soil-structure interactions and analyze deformation, stability, and groundwater flow.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API