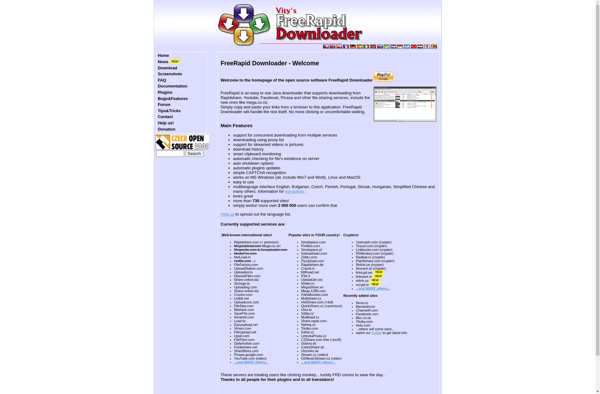
Description: FreeRapid Downloader is a free and open-source download manager for Windows. It allows downloading files from the internet via HTTP, HTTPS and FTP protocols. Key features include download acceleration, scheduling, ad-free interface, clipboard monitoring, and support for streaming media.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: upToDate Downloader is a free, open-source software that allows users to download full-text articles from the UpToDate medical database. It provides an easy way for medical students and healthcare professionals to access UpToDate content offline.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API