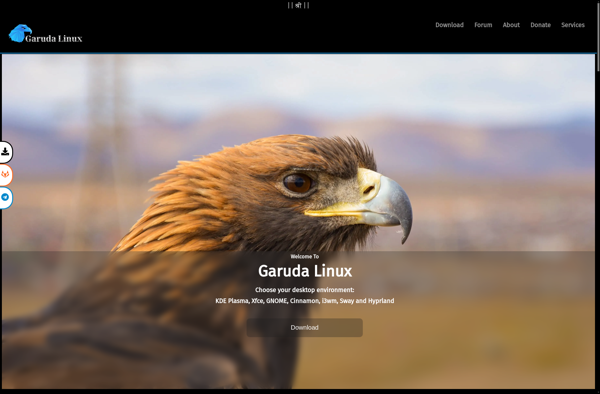
Description: Garuda Linux is a user-friendly, performance-oriented Linux distribution based on Arch Linux. It provides a polished desktop experience and easy access to latest software versions, while retaining Arch's flexibility and customization options.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: AtlasOS is an operating system designed for cloud computing and optimized for running containerized workloads. It focuses on scalability, flexibility, and ease of management.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API