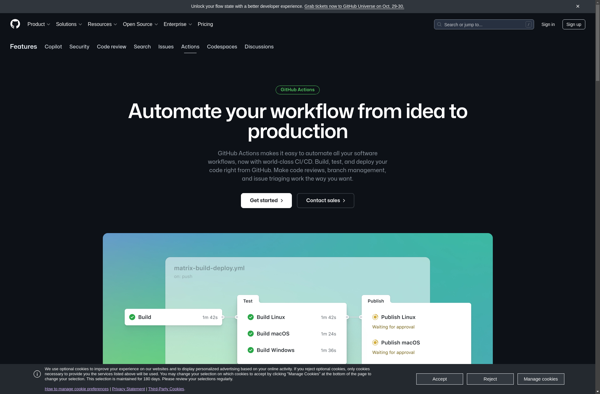
Description: GitHub Package Registry is a software package hosting service that allows you to host your software packages privately or publicly and use them as dependencies in your projects. It is integrated with GitHub's authentication and allows free hosting for public packages.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: Bintray is a distribution management platform that allows developers to host, store, manage, and distribute software packages and components. It integrates with build tools, version control systems, and package managers to automate distribution.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API