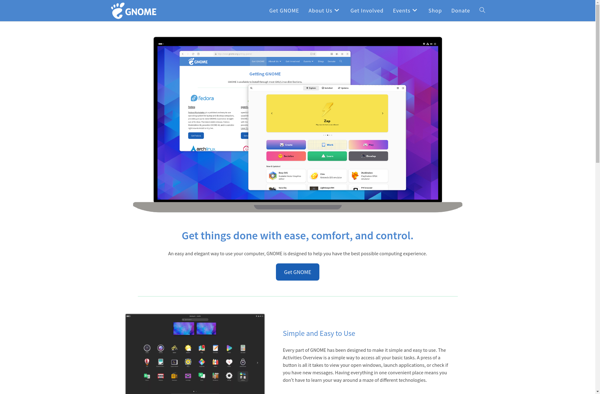
Description: GNOME is a free and open source desktop environment for Linux and Unix-like operating systems. It provides a graphical user interface and a set of applications for daily use, including a file manager, web browser, terminal, text editor, and media players.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
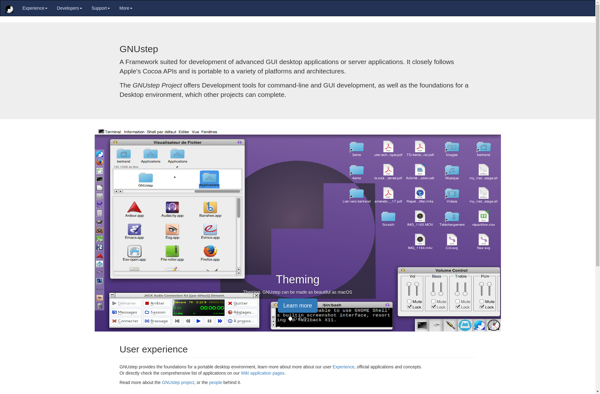
Description: GNUstep is an open source implementation of the Cocoa/Cocoa Touch frameworks used on Apple platforms like macOS, iOS, iPadOS and watchOS. It allows developers to build applications with a Cocoa-like API for other operating systems like Linux, FreeBSD and Windows.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API