Description: HardenedBSD is a security-enhanced fork of FreeBSD. It includes additional exploit mitigations like Address Space Layout Randomization and Control Flow Guard, and improves the security of existing mitigations. It's designed for hostile environments like servers and firewalls, and follows FreeBSD's stability and software support.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
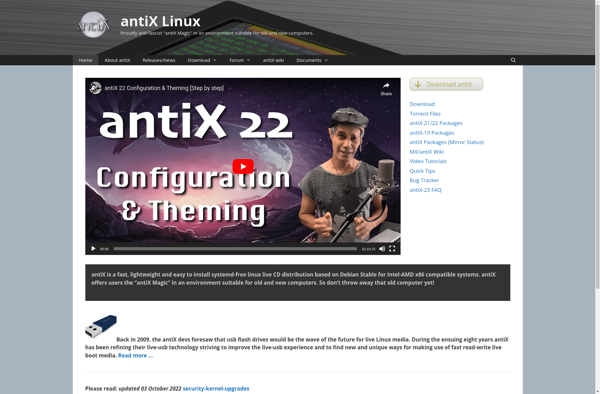
Description: antiX is a fast, lightweight and easy-to-use Linux distribution based on Debian stable. It uses the IceWM window manager and is optimized to run well on older hardware.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API