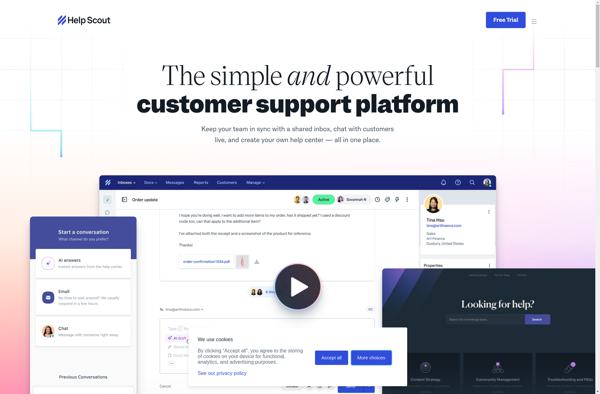
Description: Help Scout is a customer service software that provides shared mailboxes, help desk features, and automation tools to streamline support workflows. It offers email management, help desk tickets, knowledge base, reporting, and collaboration features for support teams.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: BusyBench is an open-source benchmarking software designed to evaluate the performance of PostgreSQL databases under intensive workloads. It allows simulating real-world database usage patterns to measure transactions per second, latency, and other key metrics.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API