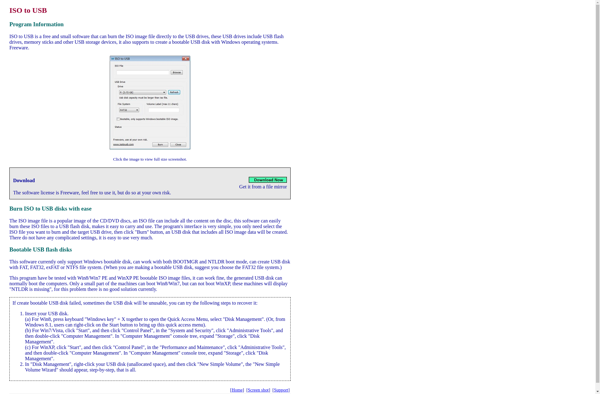
Description: ISO to USB software allows you to take an ISO disc image file and write it to a USB flash drive to create a bootable USB drive. This allows you to install operating systems or run live distributions without needing a disc drive.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
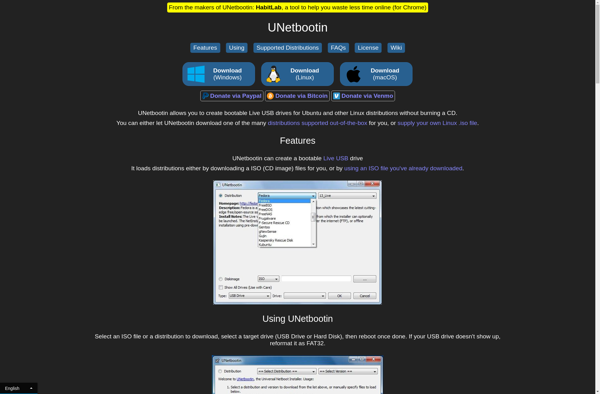
Description: UNetbootin is open-source software that allows users to create bootable live USB drives for Ubuntu, Fedora, and other Linux distributions without requiring a CD. It runs on Windows, Linux, and Mac.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API