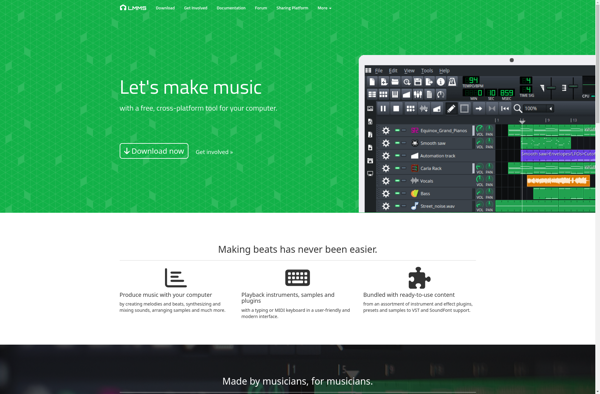
Description: LMMS is an open source digital audio workstation that allows you to produce music and sounds using virtual instruments, audio samples, and effects plugins. It has features like an easy-to-use interface, VST support, MIDI editor, and automation.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
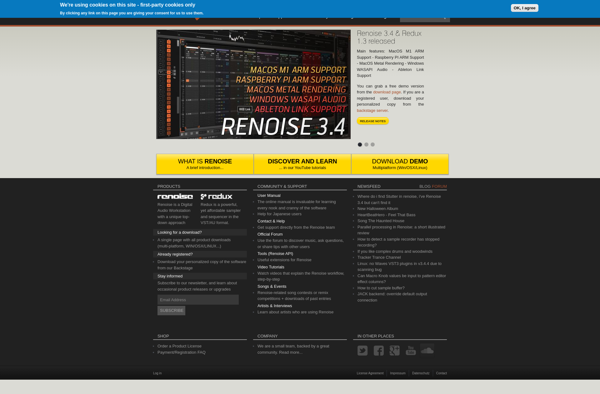
Description: Renoise is a digital audio workstation and music production software that features a tracker-based music sequencer. It allows for fast and flexible music creation and editing using a vertical timeline with rows representing instruments and note data.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API