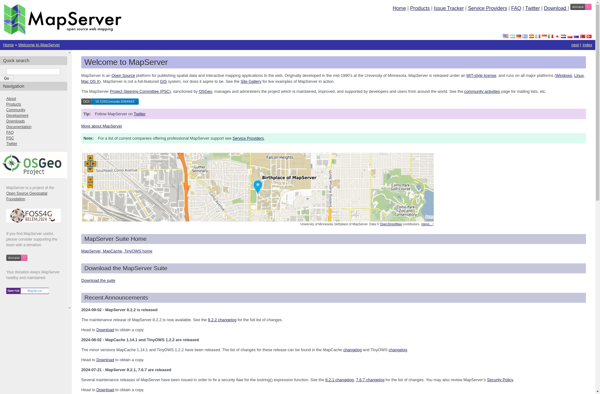
Description: Mapserver is an open source platform for publishing spatial data and interactive mapping applications to the web. It enables users to quickly build web mapping applications that leverage data from PostgreSQL/PostGIS, GeoJSON, and other sources.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
Description: ESRI Geoportal Server is an open source software that enables discovery and use of geospatial resources. It provides a standards-based metadata catalog for managing geospatial resources such as datasets, rasters, and web services.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API