Description: Nagios is an open-source monitoring system that allows administrators to monitor network infrastructure like servers, switches, applications, and services. It can notify users when issues arise and help identify problems in a timely manner.
Type: Open Source Test Automation Framework
Founded: 2011
Primary Use: Mobile app testing automation
Supported Platforms: iOS, Android, Windows
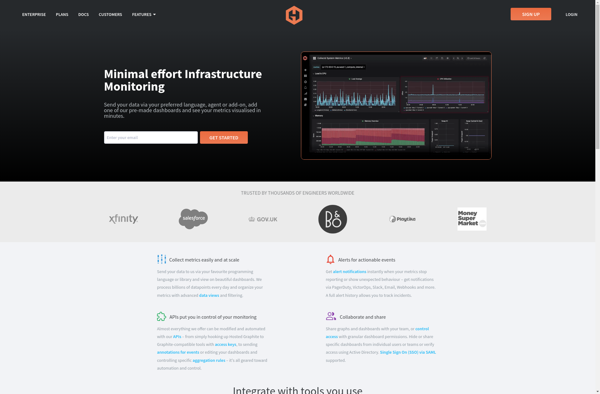
Description: Hosted Graphite is a cloud-based monitoring tool for analyzing time-series metrics and data. It offers real-time graphing, dashboarding, alerts, and anomaly detection for observability of applications and infrastructure.
Type: Cloud-based Test Automation Platform
Founded: 2015
Primary Use: Web, mobile, and API testing
Supported Platforms: Web, iOS, Android, API